| A | B |
|---|
| Where does the process of glycolysis take place? | Cytosol |
| Where does the Kreb's Cycle take place? | Inside the matrix of the mitochondria. |
| Which two molecules carry high energy electrons and deposit them into the electrons transport chain? |  |
| What are the two main reactants of cellular respiration? | ., 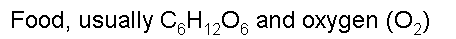 |
| What are the two main products of cellular respiration? | .,  |
| During which stages of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide molecules released? | Carbon dioxide molecules are released during the transition phase and Kreb's cycle. Basically, carbon dioxide is released whenever one of the intermediary molecules of cellular respiration gets smaller by one carbon. This happens during the transition phase when the 3-carbon molecule at the end of glycolysis is broken down into a 2-carbon molecule. This two-carbon molecule is added to a 4-carbon molecule during the Kreb's Cycle and is then stripped down to a 5-carbon and then a 4-carbon molecule during the Kreb's cycle. |
| Is molecular oxygen required for the transition phase or the Kreb's Cycle? | No, we still haven't had any need for oxygen. |
| What is the total possible net gain of ATP from one molecule of glucose that goes through aerobic cellular respiration? | 38 ATP |
| If an electron carrier molecule like NAD+ accepts two high energy electrons (and a hydrogen) from another molecule (as happens many times during respiration), it is said that the NAD+ is being __________ to NADH while the other molecule is being _______. | reduced (because the NAD+ is accepting electrons), oxidized (because the other molecule is losing electrons). Remember LEO says GER? |
| Glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of ____________ by the end of glycolysis. | pyruvic acid (a.k.a. pyruvate) |
| Where do the NADH's, generated during glycolysis, the transition phase and Kreb's Cycle, dump off their high energy electrons and hydrogen ions? | The NADH's dump off their high energy electrons to the system I proton pump of the electron transport chain. However, if the electron transport chain is backed up due to lack of oxygen, pyruvic acid from glycolysis will accept the electrons and hydrogen to form lactic acid. This way, NAD+ can be regenerated and used to keep glycolysis running. |
| What are the reactants and what are the products of the transition stage? | You start off with 2 molecules of pyruvate (pyruvic acid) and end up with 2 molecules of acetyl-CoA plus 2 molecules of carbon dioxide. In the process, two molecules of NADH are also produced from NAD+.. |
What is the name of this organelle?,  | mitochondria |
What are the folds in the membrane referred to by the letter E called?,  | Cristae |
What is the area labeled D called?,  | The matrix |
What is the area labeled C called?,  | Intermembrane space |
What is letter A pointing to?,  | The outer membrane of the mitochondrion. |
What is the letter B pointing to?,  | The inner membrane of the mitochondrion |
What is the area labeled F called?,  | That would be the cytosol of the cell. |
Where would the Kreb's Cycle take place,  | D |
Where would glycolysis take place?,  | F |
Where would the transition phase take place?,  | D |
What does letter B refer to?,  | a mitochondrion |
What does letter I refer to?,  | The cytosol |
| What happens to carbon dioxide that you generate inside cells during cellular respiration? | The carbon dioxide will diffuse out of the cell and enter the bloodstream. The bloodstream will pass the lungs where it will allow the carbon dioxide to diffuse into the lungs. From there, it is exhaled. |
| Acetyl-CoA is a __ -carbon molecule that enters the Kreb's Cycle by bonding to oxaloacetic acid, a ___-carbon molecule to form citric acid, a __-carbon molecule. | 2,4,6 |
| During the Kreb's Cycle, a ___ -carbon molecule is stripped down until it becomes a ___-carbon molecule before rejoining with acetyl-CoA to form a __-carbon molecule again. | 6,4,6 |
| What is the main purpose of the Kreb's Cycle? | The main purpose of the Kreb's cycle is to strip high energy electrons and hydrogen ions from high energy organic molecules, starting with citric acid (The Kreb's Cycle is sometimes called the Citric Acid Cycle because citric acid is the largest molecule in the cycle). |
| Which energy storing molecules are built up during the Kreb's cycle? | ., 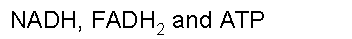 |
| During which stages of cellular respiration are ATP produced? | Glycolysis, Kreb's Cycle, and Chemiosmosis |
| During which stages of cellular respiration are NAD+ reduced to NADH? | Glycolysis, Transition stage, and Kreb's cycle |
| During which stages of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide molecules generated? | Transition stage and Kreb's cycle plus the alcohol pathway for yeast and bacteria. |
., 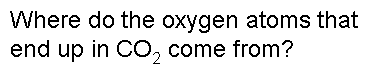 | ., 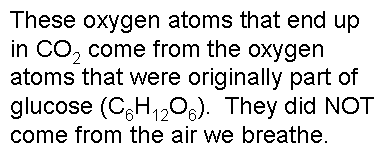 |
| Which two stages of aerobic respiration are collectively referred to as oxidative phosphorylation? | electron transport and chemiosmosis |
| The electron transport system and chemiosmosis are collectively referred to as ______. | oxidative phosphorylation |